Noun Clause As Object Of Preposition : Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why.. Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Object of the preposition examples. The object of a preposition is the noun or pronoun governed by a preposition. It can be a subject, predicate nominative, direct object, appositive, indirect object, or object of the preposition. Here the noun clause 'whether the servant had polished his shoes' is the object of the verb asked.
Here the noun clause 'whether the servant had polished his shoes' is the object of the verb asked. Here, the noun clause is receiving the direct object 'blue ribbon'. The noun clause is a clause that functions like a noun in the sentence. Keep an eye out for these words before the noun clause to indicate an object of the preposition. A word group made up of a preposition, its object, and any of the object's modifiers is called a prepositional phrase.

In this case, the noun clause is receiving the preposition 'with'.
The object of a preposition is in the objective case. Common prepositions are about, of, because of, except, but, by, for, from, in, to, toward, and with. I want to play with whoever is a good sport. Object of the preposition examples. Nouns can function as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, object of the preposition, and predicate nominatives. Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Here, the noun clause is receiving the direct object 'blue ribbon'. In the example 'with john and without me,' the words 'john' and 'me' are the objects of the prepositions. Jul 27, 2019 · in english grammar, the object of a preposition is a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that follows a preposition and completes its meaning. Dec 21, 2020 · the phrase "because of" is a preposition, so the noun clause "what he said" serves as the object of the preposition in this sentence. Noun clauses can act as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, predicate nominatives, or objects of a preposition. A word group made up of a preposition, its object, and any of the object's modifiers is called a prepositional phrase. A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun.
You know that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. Remember that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. Object of the preposition examples. The object of a preposition is in the objective case. In this case, the noun clause is receiving the preposition 'with'.
The object of a preposition is in the objective case.
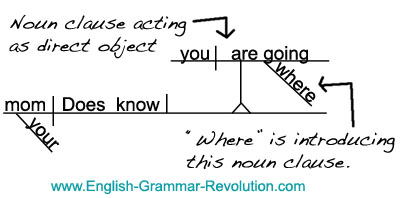
Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Jul 27, 2019 · in english grammar, the object of a preposition is a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that follows a preposition and completes its meaning. ('blue ribbon' is the direct object because it is receiving the verb 'award'.) example 3. The object of a preposition is usually the noun or pronoun immediately to the right of the preposition. Here the noun clause 'where he has gone' is the object of the verb know. Nouns can function as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, object of the preposition, and predicate nominatives. The object of a preposition is the noun or pronoun governed by a preposition. A content clause, also known as a noun clause, provides content implied or commented upon by its main clause. Here the noun clause 'what he says' is the object of the preposition on. You also know that a preposition is a word that comes before one noun to show its relationship to another word in the phrase or clause. It can be a subject, predicate nominative, direct object, appositive, indirect object, or object of the preposition. Keep an eye out for these words before the noun clause to indicate an object of the preposition. Object of the preposition examples.
The object of a preposition is usually the noun or pronoun immediately to the right of the preposition. You know that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. In this case, the noun clause is receiving the preposition 'with'. Jul 27, 2019 · in english grammar, the object of a preposition is a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that follows a preposition and completes its meaning. Common prepositions are about, of, because of, except, but, by, for, from, in, to, toward, and with.
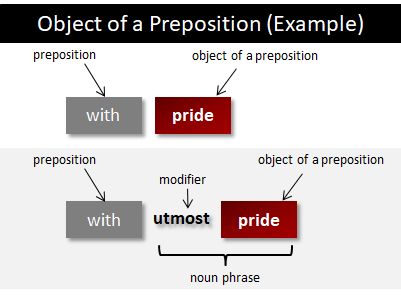
In the example 'with john and without me,' the words 'john' and 'me' are the objects of the prepositions.
In this case, the noun clause is receiving the preposition 'with'. Common prepositions are about, of, because of, except, but, by, for, from, in, to, toward, and with. A word group made up of a preposition, its object, and any of the object's modifiers is called a prepositional phrase. You know that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. Here the noun clause 'what he says' is the object of the preposition on. Other times, noun clauses can act as the object of a preposition in the independent clause. A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun. Remember that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. It can be a subject, predicate nominative, direct object, appositive, indirect object, or object of the preposition. The object of a preposition is in the objective case. Keep an eye out for these words before the noun clause to indicate an object of the preposition. Here, the noun clause is receiving the direct object 'blue ribbon'. A content clause, also known as a noun clause, provides content implied or commented upon by its main clause.
Nouns can function as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, object of the preposition, and predicate nominatives noun clause. Other times, noun clauses can act as the object of a preposition in the independent clause.

0 Komentar